THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENTIATED LEARNING ON STUDENTS’ COMPUTATIONAL THINKING SKILS IN MATHEMATICS LEASSONS
Abstract
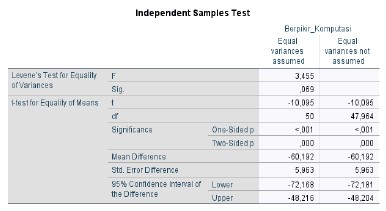
This study aims to analyze the effect of differentiated learning on students' computational thinking skills in mathematics. This research was conducted at MAN Sibolga, located in Sibolga in the odd semester of the 2024/2025 school year. The method used was a quasi-experiment with a pretest-posttest non-equivalent control group design. The sampling technique was carried out using purposive sampling technique, where class XI-A was the experimental class with 26 students, while class XI-F was the control class with 26 students. Data collection regarding students' computational thinking skills used a test instrument consisting of five description items that had gone through the validity and reliability testing process. The indicators of computational thinking ability studied included problem decomposition, abstraction, algorithm thinking, generalization, and debugging. The results showed that students taught using differentiated learning model had higher computational thinking ability compared to students taught through lecture learning model.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFDOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.31000/prima.v9i1.13100
Article Metrics
Abstract - 1556 PDF - 892Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Prima: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika
Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika
Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan
Universitas Muhammadiyah Tangerang
Jl. Perintis Kemerdekaan I/33, Cikokol
Kota Tangerang, Indonesia
e-mail: primajpm@gmail.com
Prima: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (p-ISSN: 2579-9827 | e-ISSN: 2580-2216) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.